chatbot.yaml configuration file
chatbot.yaml is the main chatbot configuration file. It contains all configurable properties for the project, such as:
- The name of the main script file.
- Information on imported dependencies.
- NLU configuration.
- The list of included test files.
This article describes the properties which can be set in chatbot.yaml and their purpose.
Script entry point
entryPoint: main.sc
This property sets the script entry point — the file which is the first to load when the chatbot is deployed.
The file must be located in the src folder and is conventionally named main.sc or entryPoint.sc.
require tag for importing files.entryPoint is a required property.Bot name
name: echo-bot
This property sets the bot name, by which it will be referenced in deploy logs and other system messages. If the property is missing, the internal project name will be used instead.
NLU settings
Bot engine
botEngine: v2
This property sets the chatbot engine version.
v2) enables the NLU core for natural language understanding.
This is the recommended setting for all new projects.v2, the legacy bot engine (v1) will be used instead.
This engine allows only patterns for NLU.Bot language
language: en
This property sets the language the bot will understand. The value should be a language ISO code.
Thresholds
You can set thresholds:
Intent thresholds
nlp:
intentNoMatchThresholds:
phrases: 0.2
patterns: 0.2
The phrases and patterns fields in the nlp.intentNoMatchThresholds section set the thresholds for intents.
This is how the classifier works:
-
The user sends a request to the bot.
-
When generating hypotheses, the classifier compares the request with patterns and training phrases individually. It calculates the probability for each of the hypotheses.
tipA hypothesis is the result of the classifier. When the classifier generates a hypothesis, it determines the extent to which the user’s request corresponds to a particular intent. Thus, the classifier expresses the degree of its confidence that this intent really contains a phrase or a pattern from the user’s request. -
If the hypothesis probability is less than the threshold of
phrasesorpatterns, it is discarded and ignored during subsequent request processing and defining the state in the script.
In other words, intentNoMatchThresholds sets the minimum required similarity of the request to the intent phrases or intent patterns.
The closer its value is to 1, the stricter are the matches that it requires.
The default value of phrases and patterns is 0.2.
This value is used if you do not specify another one for any of the fields.
Pattern threshold
Patterns can be specified in the q and q! tags. By default, these patterns are taken into account with any weight.
The patternNoMatchThreshold parameter in the nlp section allows you to set a threshold value for the patterns:
nlp:
patternNoMatchThreshold: 0.5
If the match weight of a pattern is less than this value, the pattern is ignored during request processing. The closer the threshold value is to 1, the more accurate matches are required.
$context.nBest length
nlp:
nbest: 3
nbestPatterns: 1
nbestIntents: 2
Properties beginning with nlp.nbest determine the number of activation rules
available from the script via the $context object.
- The
nbestproperty sets the length of$context.nBest— an array of activation rules of all possible types (patterns, intents, and examples) triggered for the request. The default value is1. nbestPatternssets the length of$context.nBestPatterns— an array of activation rules only triggered by patterns. The array is unavailable if this property is omitted.nbestIntentsis used for intents. It works the same asnbestPatterns.
Regular expression modes
You can use regular expressions in the script via $regexp and $regexp_i.
Default mode
By default, the special characters and punctuation marks are ignored before and after the expression.
Examples of patterns and the strings that they will be triggered by:
| Pattern | String |
|---|---|
$regexp<Hello> | Hello! |
$regexp<^\d+$> | + 50%. |
Monday $regexp<\d\d:\d\d> | Monday, 12:30? |
Strict mode
To enable the mode, specify this setting in chatbot.yaml at the top nesting level:
strictRegexp: true
In this mode, regular expressions are triggered only if the string matches the expression completely:
| Pattern | String |
|---|---|
$regexp<Hello> | Hello |
$regexp<^\d+$> | 50 |
Monday $regexp<\d\d:\d\d> | Monday 12:30 |
This mode is not supported in the following cases:
-
If you use a regular expression in a named pattern:
patterns:
$num = $regexp<\d+>For example, this
$numpattern will be triggered by the100%string. -
If any other pattern element is specified after the regular expression. For example,
$regexp<\d+> ~goodswill be triggered by50% of goods.
Request processing limits
Request length limit
nlp:
lengthLimit:
enabled: true
symbols: 100
words: -1
nlp.lengthLimit sets a length limit on requests processed by the bot:
enabledenables or disables the limit.symbolsis the maximum number of characters contained in the request.wordsis the maximum number of words in the request. This limit is disabled if set to-1.
By default, the limit is enabled and set to 400 characters. The word limit is disabled.
lengthLimit event will be triggered.Request processing timeout
nlp:
timeLimit:
enabled: true
timeout: 500
nlp.timeLimit sets a limit on the time allotted for processing the request:
enabledenables or disables the limit.timeoutis the maximum time allowed for request processing, in milliseconds.
By default, the limit is enabled and set to 10000 (10 seconds).
timeLimit event will be triggered.XML tests
tests:
include:
- "authorization.xml"
- "integration-tests/*.xml"
exclude:
- "broken.xml"
caseSensitive: false
You can use XML tests to verify the chatbot script by emulating client requests and asserting that bot responses behave as expected.
By default, all tests contained in the test folder are executed.
You can override this behavior by setting the values for include and/or exclude in the tests section:
include— only the tests from the files matching the patterns listed in this subsection will be executed.exclude— all the files matching the patterns listed in this subsection will be excluded from execution.
The caseSensitive property determines whether patterns should be case-sensitive. It is true by default.
Dependencies
dependencies:
- name: common
type: git
url: https://<repository>
version: heads/master
The dependencies section contains a list of project dependencies.
Action tags
customTags:
- src/blocks/SumTwoNumbers/block.json
The customTags section defines the list of custom action tags used in the project.
Custom reactions
customBlocks:
- src/blocks/video.json
The customBlocks section defines the list of custom reactions used in text campaigns.
Error messages
messages:
onError:
locales:
en: Failed on request processing.
de: Es ist etwas schiefgelaufen.
defaultMessage: Something went wrong.
# defaultMessages:
# - Sorry, the bot just crashed.
# - An error occurred when processing your request.
The messages.onError allows setting the text of the message the chatbot will send if any errors occur in the script.
The locales subsection should contain messages localized based on user locale data.
In this subsection, the keys are language ISO codes, and the values are the message texts themselves.
In the defaultMessage property, you can configure the text
which will be sent by default if the necessary language or the locales section itself is missing.
You can also set a list of such messages in defaultMessages, in which case a random error message will be chosen every time.
messages.onErrorsection is missing, the bot will not respond at all if an error occurs.Injector
injector:
catchAllLimit: 10
api:
protocol: https
host: example.com
port: 443
Use the injector section to set up the chatbot configuration.
All properties will be accessible from the chatbot script via the $injector variable.
SMTP server configuration
Use the injector.smtp section to configure the settings for the SMTP server
that will be used for sending email messages via the $mail.sendMessage method.
injector:
smtp:
host: smtp.tovie.ai # SMTP server host
port: 2525 # SMTP server port
user: user@tovie.ai # SMTP server user
password: qwerty # SMTP server password
from: bot@tovie.ai # Email sender
# Optional properties
hiddenCopy: admin@tovie.ai # Email hidden copy recipient
# You can specify a list of recipients:
# hiddenCopy:
# - admin@tovie.ai
# - support@tovie.ai
debugMode: true # Whether debug mode is on or off
Slot filling configuration
In the injector.slotfilling section, you can specify the parameters for the slot filling interruption:
injector:
slotfilling:
maxSlotRetries: 5
stopOnAnyIntent: true
stopOnAnyIntentThreshold: 0.2
stopOnTimeout: true
stopOnTimeoutValue: 3600
Other settings
Request modification
nlp:
modifyRequestInPreMatch: true
When enabled, the nlp.modifyRequestInPreMatch property allows modifying the request content in the preMatch handler, e.g. changing the request text.
Word tokenization in patterns
tokenizeWordsInPatterns: true
The tokenizeWordsInPatterns property enables word tokenization in patterns for languages without word separators.
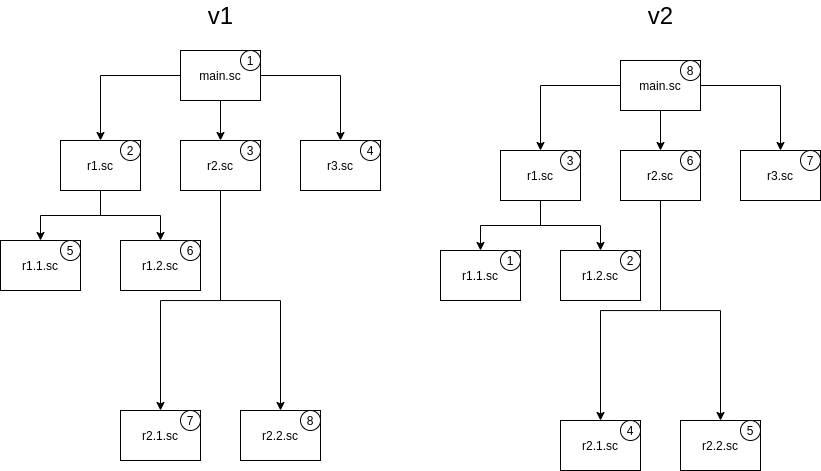
File import strategy
scenarioLoadStrategy: v2
The scenarioLoadStrategy property sets the strategy for loading files into the script consisting of multiple files.
The property has two possible values: v1 (set by default) and v2.
When using the v1 strategy, required files are loaded in the top-to-bottom order in the dependency tree, while v2 makes them load from bottom to top.
The following example illustrates the difference.
The main.sc file imports r1.sc, r2.sc, and r3.scusing the require tag, and both r1.sc and r2.sc also have two imported files.
When the script is deployed, the files will be loaded in the order illustrated in the image below.
Influence of context distance on intent score
nlp:
considerContextDepthInStateSelectionV2: false
The nlp.considerContextDepthInStateSelectionV2 property determines
whether the context distance to states triggered by the intent/intent! tag or the intentGroup/intentGroup! tag should be taken into account when calculating intent scores.
true(default value) — context distance is used for calculating intent scores and selecting the target state.false— intent scores do not depend on context distance and are calculated the same way in all states.