Entities
An entity is a unit of the NLU core. It is a sequence of words that share meaning or fall under a common rule. For example, it can be a name, a timestamp, or a location.
You can use either custom or system entities. All enabled entities can be used for script development.
Custom entities
Custom entities are entities that the developer constructs and configures in the entity editor.
Open a project, then select Tovie NLP → Entities in the dashboard. You have navigated to the project entities dictionary.
Entity settings
Select Create entity and specify the entity name.
The entity name must not match the name of a pattern that was created using $entity<> and converter.
For example, if a project has an Example entity and an $Example pattern, it might cause errors during the script execution.
Recognized
Select the recognized button above the entity name to have the entity recognized in the chat. Select this button again to disable recognition.
Let us have a look at how the script works with different settings:
| State | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Entity is recognized in the conversation. The intent referring the entity will be triggered, the slot will be filled, metadata for that entity will appear in the script. |
| Disabled | Entity is not recognized in the conversation. The intent referring the entity will not be triggered, the slot will not be filled, metadata for that entity will not appear in the script. |
Client
Select client under the entity name to make its value unique for each client. Select this button again to disable this feature.
Let us have a look at how the script works with different settings:
| State | Behavior |
|---|---|
| Enabled | Entity values and metadata are unique for each bot client. Data obtained from clients are filled in via the API or in the chat. |
| Disabled | Entity values and metadata are specified by the bot developer and are common for all the clients of the bot. |
Additional settings
Word normalization
When the Normalize words setting is enabled, all the words contained in the request are normalized before being searched for entities.
Fuzzy search
By default, the search for entities in client requests is performed in “strict” mode: if an entity name consists of several words, they are all required to be contained in the request one after another.
However, if the Use fuzzy/substring search setting is enabled, the search for entities allows for a greater request diversity:
- Words comprising the entity name can have unrelated words in between them.
- Some words comprising the entity name can be omitted altogether.
@City entity matches the cities of the world. The record for New York has new york as its only synonym. However, if the entity has fuzzy search turned on, the entity will be found in such requests as york as well as new freaking york.Intent expansion
The Automatically expand intents setting is best explained by example:
- The
@agententity is defined with a number of synonyms, e.g. agent, helper, support. - The
/Switchintent is defined and trained on a single phrase, transfer me to an agent. - If the client says transfer me to support, the
/Switchintent will be recognized.
Dictionary
An entity is defined via a set of values that it can take. In the dictionary window, select Add record. Select one of the methods for specifying the values:
- Synonyms — specify the set of synonyms: all the spelling variants which will be equivalent to this value.
- Pattern — specify the pattern: a formal rule that describes keywords and expressions. Use basic pattern elements.
You can also specify DATA: reference data on the entity, in the string or JSON format.
System entities
System entities are built-in entities that the developer can activate in the entity editor.
You can activate the recognition of system entities. Open a project and select Editor → Entities → System entities in the dashboard.
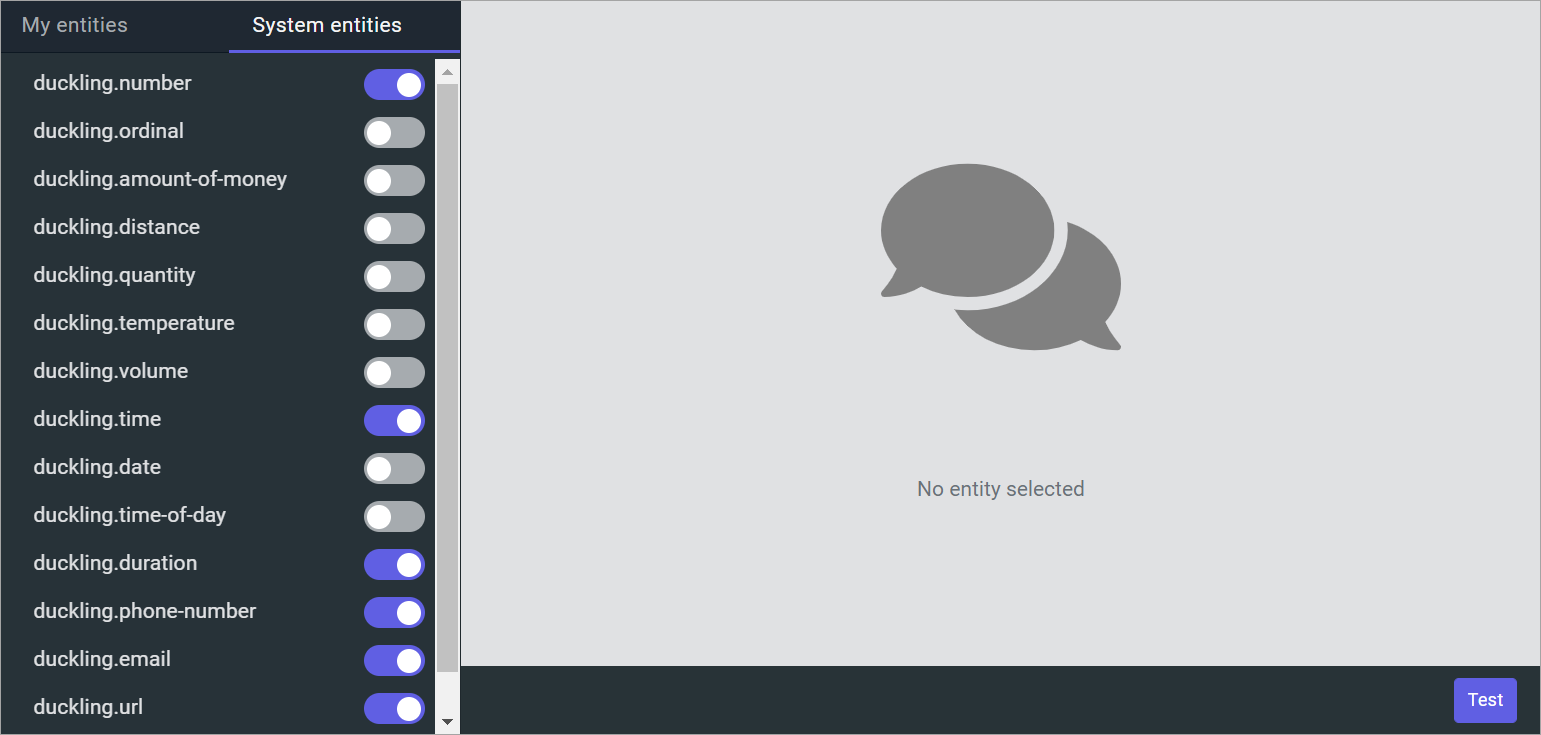
To activate a system entity, enable the checkbox next to its name. As soon as the status is changed, Tovie Platform will start recognizing this entity in the messages sent to the bot.